Inductor
Basic Electronics Part 1 – Passive ComponentsAn inductor is simply a coil of wire. The basic function is to concentrate the magnetic field of electric current in the coil. More importantly, an induced voltage is generated when the current with its associated magnetic field changes in value or direction. Putting an inductor in a circuit greatly compensates for the sudden change in current that may occur. The voltage across an inductor in a circuit is equal to zero.
The effectiveness of an inductor is determined by four factors:
- The number of coils - More coils means more inductance.
- The material that the coils are wrapped around or the so-called core
- The cross-sectional area of the coil - More area means more inductance.
- The length of the coil - A short coil means narrower (or overlapping) coils, which means more inductance.
A transformer is composed of two or more coil windings. Induced current is produced when there is a current change in any of the windings. The purpose of the transformer is to increase or decrease the amount of voltage between the windings. The transformer, however, operates in AC (Alternating current) voltage only.
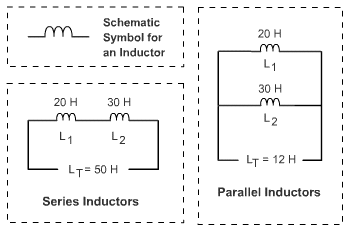
When dealing with a series-parallel connection, the inductance is obtained by applying the rules in series and in parallel connections one after another.
Previous | Next

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< back to Home